

CMD LIST DIRECTORY CONTENTS PLUS
This option shows all the files and folders in the specified directory plus all of the files and folders contained within any subdirectories of that specified directory. The data stream itself is listed in a new row, under the file, and is always suffixed with $DATA, making them easy to spot. The /r option shows any alternate data streams (ADS) that are part of a file.
CMD LIST DIRECTORY CONTENTS WINDOWS
The easiest way to view or change a file's ownership from within Windows is via the Advanced button in the Security tab when looking at the file's Properties. Use this switch to display the owner of the file or folder in the results. Using /p is very similar to using the dir command with the more command. This option displays the results one page at a time, interrupted with a Press any key to continue. = Use this as a prefix with any of the above values to reverse the order ( -d to sort by newest first, -s for largest first, etc.). G = group directory first, followed by files Use this option with one or more of the following values (colon is optional, no spaces needed) to sort the dir command result in the specified manner:
When executed alone, /o lists directories first, followed by files, both in alphabetical order. Use this option to specify a sort order for the results.
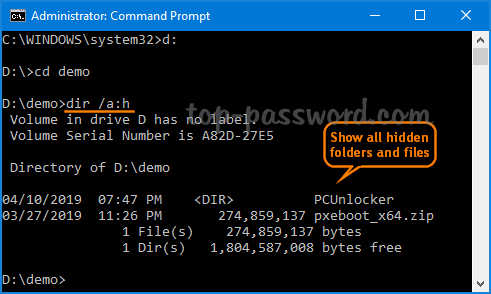
Since this is the default behavior, the practical use is /-n which produces columns in the file or folder name > directory > file size > date > time order. This switch produces a result with columns in the date > time > directory > file size > file or folder name column structure. Use this option to show all folder and file names in lowercase. Standard dir command header and footer data remain the same. Items are listed top-to-bottom and then across columns. Use /d to limit the items displayed to just folders (contained within brackets) and file names with their extensions. This is the default behavior on most computers, so the practical use is /-c to disable the thousands separator in results. This switch forces the use of the thousands separator when the command is used in a way that shows file sizes. Use this option to show the dir results using "bare" format, which removes the typical header and footer information, as well as all the details on each item, leaving only the directory name or file name and extension. = Use this as a prefix to any of the above attributes to exclude items with those file attributes from the results. Use /a with one or more of the following attributes (colon is optional, no spaces needed) to show only those types of files in the command result: When executed alone, this switch shows all types of files and folders, including those with file attributes that typically prevent them from showing up in Command Prompt or in Windows. See the Dir Command Examples section below if this isn't clear. All three are optional since the command can be executed alone. This is the drive, path, and/or filename that you want to see results for.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
